Smartphones today hold far more than contacts and photos. They store location history, private conversations, browsing habits, work data, and even biometric signals. At the center of all this data lies one critical system: app permissions.
Android has spent the last few years quietly redesigning how permissions work behind the scenes. The goal is simple but powerful. Apps should only access sensitive data when they actually need it, and users should not have to micromanage every installed app.
This is where Android’s background permission management, especially the auto-reset feature, plays a major role.
In this detailed guide, we will break down how Android manages app permissions in the background, how auto-reset works, why it exists, what changed in recent Android versions, and how users can take full control without breaking important apps.
Also Read: Why Android Settings Change Automatically After Updates (Full Explanation)
Why Background App Permissions Matter More Than Ever
Most users focus on what apps do while they are open. But from a privacy and security standpoint, what apps do when you are not using them is often more important.
Historically, once you granted permissions like location, camera, or microphone, many apps retained that access indefinitely. Even if you stopped using the app, it could still sit quietly on your phone with powerful permissions intact.
This created several risks:
- Forgotten apps retaining access to sensitive data
- Increased attack surface if an app became compromised later
- Unnecessary background activity affecting battery and performance
- Users losing visibility over which apps could access what
Android’s modern permission system was designed to fix these issues gradually, without overwhelming users.
A Quick Evolution of Android Permission Management

To understand how Android manages app permissions today, it helps to see how we got here.
Before Android 6.0: Install-Time Permissions
In older Android versions, permissions were granted at install time. You either accepted all permissions or you did not install the app at all. Users had little real control.
Android 6.0 and Above: Runtime Permissions
Android 6.0 introduced runtime permissions. Apps had to ask for sensitive permissions while running, and users could deny them individually.
This was a major shift, but it still left a gap. Permissions stayed granted forever unless the user manually revoked them.
Android 10 and 11: Context-Based Access
Later versions added options like:
- Allow only while using the app
- Ask every time
- One-time permissions
But unused apps could still hold permissions silently.
That is where auto-reset permissions entered the picture.
What Is Android’s Auto-Reset Permissions Feature?
Android’s auto-reset permissions feature is a background privacy mechanism that automatically revokes sensitive permissions from apps you have not used for a long time.
In simple terms, if an app has been sitting idle on your phone for months, Android assumes you no longer actively trust it with sensitive data.
Instead of waiting for you to clean things up manually, the system does it for you.
Introduced in Android 11
Auto-reset was officially introduced in Android 11 as a default behavior for modern apps. Later, Google expanded it to older Android versions using Google Play services.
This means the feature is not limited to the latest phones only.
How Auto-Reset Works Behind the Scenes
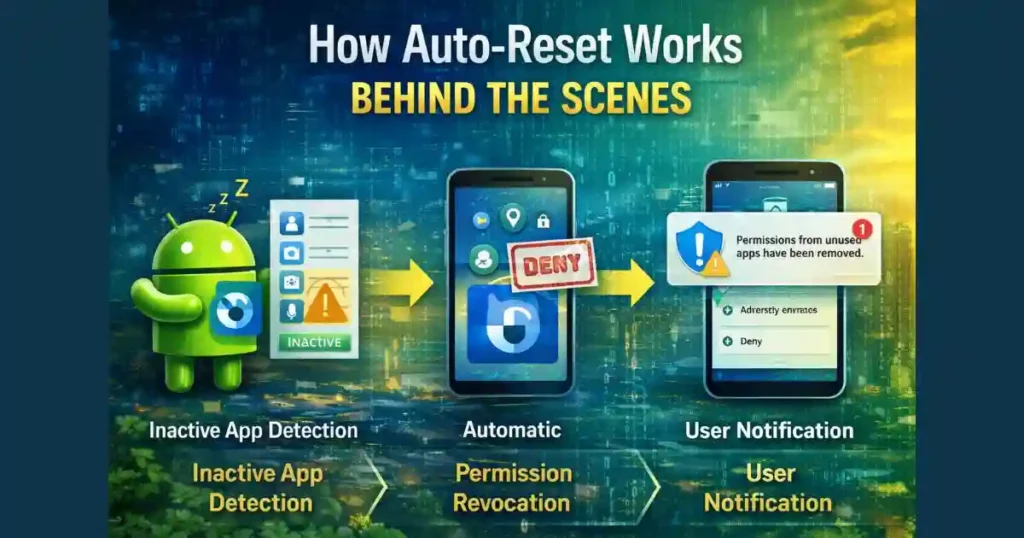
Android does not randomly revoke permissions. The process follows a clear logic.
Inactive App Detection
The system continuously tracks app usage patterns. If you do not open or interact with an app for several months, Android flags it as inactive.
This inactivity period is typically around 90 days, though it may vary slightly depending on system optimizations.
Automatic Permission Revocation
Once an app is marked inactive, Android resets its sensitive runtime permissions back to a Deny state.
This usually includes permissions such as:
- Location
- Camera
- Microphone
- Contacts
- Storage access
From the system’s perspective, it is as if you manually revoked those permissions.
User Notification
Android generally informs users when permissions are auto-reset. You may see a notification explaining that unused apps had their permissions removed.
This keeps the process transparent rather than silent.
Re-Granting Permissions on Next Use
When you eventually open the app again, it behaves like a fresh install from a permission standpoint.
The app must ask for permissions again, and you get a chance to decide based on whether you still trust or need it.
Why Android Auto-Resets Permissions Instead of Deleting Apps
A common question is why Android does not simply uninstall unused apps.
The reason is balance.
Many users keep apps for occasional use, travel, emergencies, or specific situations. Removing apps entirely could cause frustration.
Auto-reset focuses on risk reduction, not removal. It limits data access while keeping the app available if you need it later.
Scope and Availability Across Android Versions

Android 11 and Higher
For apps targeting Android 11 or newer, auto-reset is enabled by default. Developers are expected to design apps assuming permissions may be revoked after inactivity.
Android 6.0 to Android 10
Google expanded auto-reset support to older Android versions via Google Play services.
For older apps targeting legacy APIs, users may need to manually enable the feature using a toggle labeled something like:
- Remove permissions if app isn’t used
Nearly Universal Coverage
Because Play services updates run independently of full OS updates, even many older devices now support this feature.
This makes Android’s permission system more consistent across devices.
App Hibernation in Android 12 and Later
Starting with Android 12, auto-reset became part of a broader concept called app hibernation.
What Is App Hibernation?
App hibernation goes beyond permissions. When an app remains unused for a long time, Android may:
- Reset its sensitive permissions
- Delete temporary and cache files
- Restrict background execution
- Free up storage and system resources
This approach improves both privacy and performance.
Why Google Added Hibernation
Unused apps often consume storage and occasionally wake up in the background. Hibernation ensures inactive apps become truly dormant without user intervention.
Exceptions: When Auto-Reset Does Not Apply
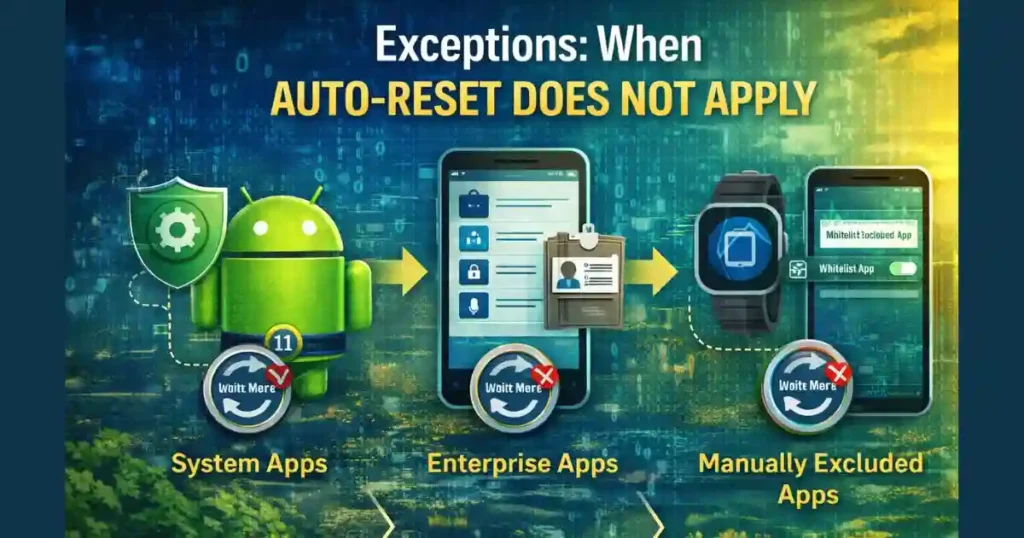
Android understands that not all apps can follow the same rules.
System Apps
Core system apps and essential services are typically exempt. Auto-resetting them could break basic phone functionality.
Enterprise and Work Profile Apps
On company-managed devices, certain permissions may be fixed by enterprise policy. Android cannot auto-revoke those permissions.
Manually Excluded Apps
Users can whitelist specific apps that need long-term background access.
Examples include:
- Smartwatch companion apps
- Fitness trackers
- Medical monitoring apps
- Security and automation tools
These apps may appear inactive but still require permissions to function correctly.
How Android Manages App Permissions in the Background Overall
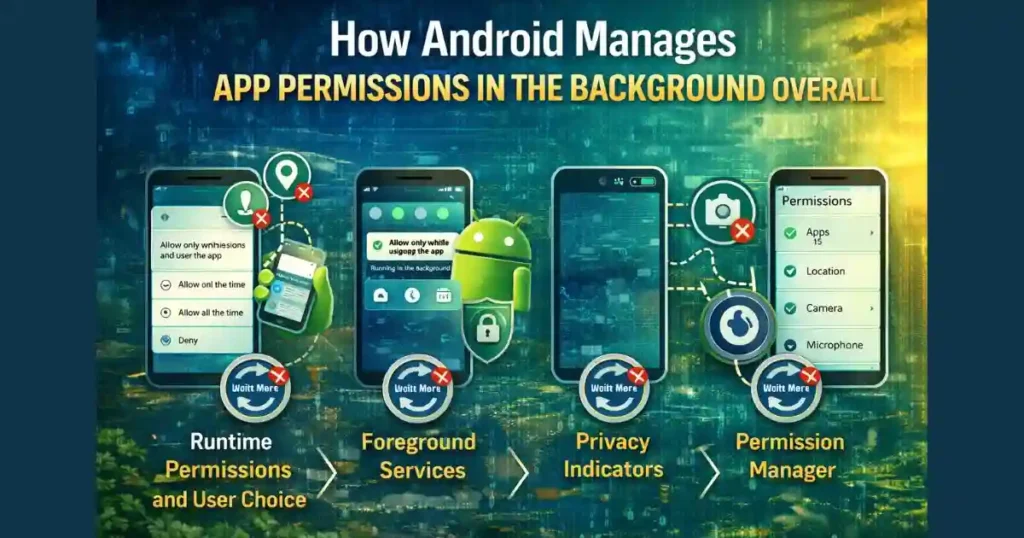
Auto-reset is only one part of a larger system. Android combines multiple mechanisms to manage background permissions responsibly.
Runtime Permissions and User Choice
Whenever an app requests sensitive access, Android presents clear options.
Common choices include:
- Allow only while using the app
- Ask every time
- Don’t allow
For location access, Android provides even more granular control.
“Allow All the Time” and Why It Is Restricted
Location permissions deserve special attention because they are often abused.
On modern Android versions, users cannot grant background location access directly from the first permission pop-up.
Instead, Android forces an extra step through system settings. This ensures that granting continuous location access is a deliberate choice.
This design helps prevent accidental over-permissioning.
Foreground Services and Persistent Notifications
If an app needs to run in the background while using sensitive permissions, it must declare a foreground service.
This comes with a visible, persistent notification.
The notification serves two purposes:
- Transparency for the user
- Accountability for the app
You always know when an app is actively doing something in the background.
Privacy Indicators in Android 12 and Above
Another important layer is real-time transparency.
Whenever an app uses the camera or microphone, Android shows a small indicator in the status bar.
This applies even when the app is running in the background, giving users immediate awareness.
Permission Manager: Centralized Control
Android includes a Permission Manager, which acts as a control hub.
You can review permissions:
- By app
- By permission type
This makes it easier to spot patterns, such as which apps have location access or microphone access.
Managing App Permissions Manually: Step-by-Step
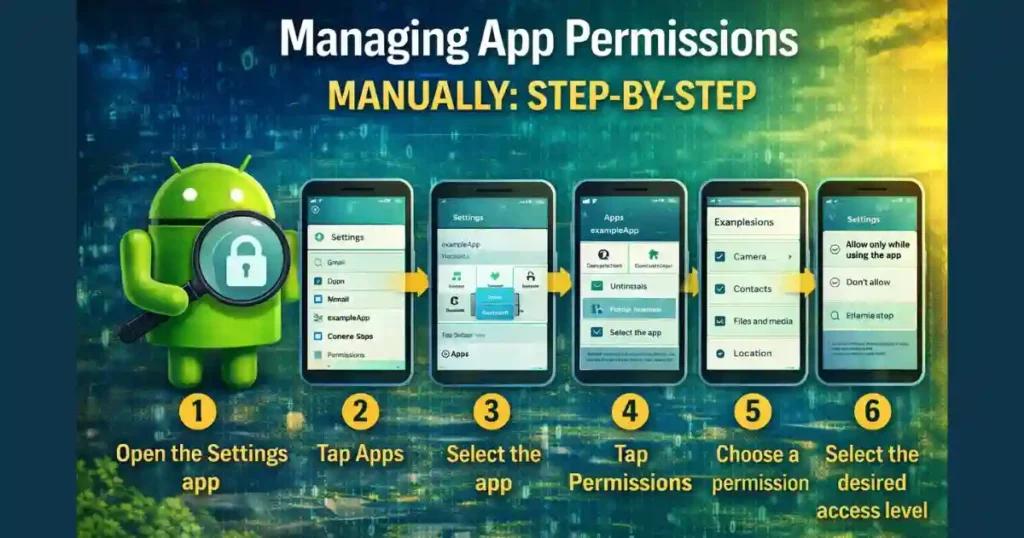
If you want full control over background access, Android gives you the tools.
Open App Permission Settings on Android
- Open the Settings app
- Tap Apps or Apps & notifications
- Select the app
- Tap Permissions
- Choose a permission like Location or Microphone
- Select the desired access level
For location, you may need to open a dedicated page to manage background access.
Battery Optimization and Background Behavior
Permissions are not the only factor affecting background activity.
Battery optimization settings can restrict how apps run even if permissions are granted.
Users can usually navigate to:
Settings > Battery > App battery usage
From there, apps can be set to restricted, optimized, or unrestricted modes.
Also Read: How Android Decides Which Notifications Are Silent or Important
Common Queries Explained
How Android Manages App Permissions in the Background Samsung
Samsung devices follow the same core Android permission system, with some UI differences. Features like auto-reset, permission manager, and hibernation still apply, though menu names may vary slightly.
App Permission Setting
App permission settings allow users to grant, deny, or limit access to sensitive features. Modern Android versions emphasize contextual access rather than permanent permissions.
Open App Permission Settings Android
Users can open app permission settings through the system settings by selecting an app and tapping on Permissions. Some manufacturers add shortcuts within the app info screen.
Open App Permission Settings Android Programmatically
Developers can redirect users to app permission settings using system intents. This is commonly used when permissions are essential for core app functionality.
What App Permissions Should I Allow
Only allow permissions that are necessary for the app’s core function. Be cautious with background location, microphone, and contacts unless you fully trust the app.
App Permission Manager
The App Permission Manager provides a centralized overview of all permissions granted across apps, helping users spot excessive access.
App Permission Manager Android
On Android, the Permission Manager is typically found under Privacy or Security settings, depending on the version.
Android Permissions List
Android permissions include categories like location, camera, microphone, contacts, storage, phone, and sensors. Each category has different risk levels.
Why Auto-Reset Is a Big Deal for Privacy

Auto-reset quietly solves a problem most users never think about.
People install apps for one-time needs and forget about them. Without auto-reset, those apps retain long-term access.
By revoking permissions automatically, Android reduces long-term privacy exposure without demanding constant user action.
Potential Downsides and User Awareness
Auto-reset is not perfect.
Some users may open an app after months and find features suddenly broken due to missing permissions. This can cause confusion if users are not aware of the feature.
However, Android usually provides prompts and explanations, and permissions can be re-granted instantly.
Best Practices for Users
- Periodically review permission settings
- Whitelist apps that genuinely need background access
- Be cautious with “Allow all the time” permissions
- Pay attention to system notifications about auto-reset
Best Practices for Developers

Developers should assume permissions may be revoked and design apps accordingly.
Apps should:
- Handle permission loss gracefully
- Explain clearly why permissions are needed
- Avoid requesting unnecessary background access
The Bigger Picture: Android’s Privacy Direction
Android’s approach reflects a broader industry shift.
Instead of relying entirely on user vigilance, the system itself actively reduces risk.
Auto-reset, hibernation, privacy indicators, and permission managers together form a layered defense model.
FAQs: How Android Manages App Permissions
Does auto-reset delete my app data?
No. Auto-reset only revokes permissions. App data remains unless app hibernation removes temporary files.
Can I turn off auto-reset for specific apps?
Yes. You can disable it per app using the “Remove permissions if app isn’t used” toggle.
Does auto-reset affect system apps?
Usually no. Core system apps are exempt.
Is auto-reset available on older Android phones?
Yes. Google expanded it to Android 6.0 and above via Play services updates.
Will apps notify me when permissions are reset?
Android generally shows a notification when permissions are auto-reset.
Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available information about Android’s permission system and platform behavior. Features and settings may vary depending on device manufacturer, Android version, and regional updates. Users should refer to official Android documentation or device-specific support pages for the most accurate details.
Also Read: What Happens When You Force Stop an App on Android? Real Effects Explained

Raj Prajapati is a skilled content writer dedicated to creating clear, step-by-step guides on technology, Health, and everyday solutions. With a focus on user-friendly and SEO-optimized content, he simplifies complex topics, helping readers learn and solve problems effortlessly.

