Online distractions are growing faster than ever. Whether it is social media, streaming platforms, or adult and harmful websites, unrestricted access can interrupt productivity, expose children to inappropriate content, and even open the door to cybersecurity threats. Because of this, many users look for ways to take control of their internet environment.
While extension-based blockers are popular, not everyone wants to depend on third-party add-ons. Some users are prevented from installing extensions at school or work, and others simply want stronger system-level control. This is why learning how to block websites on your browser without extensions has become an important digital skill.
In this guide, we explore every reliable method — from modifying hosts files and router settings to using DNS filtering and built-in privacy features — with complete context, advantages, possible limitations, and safety recommendations.
Unlike short tutorials, this article breaks down the reasoning behind each method so users can confidently decide which approach fits their environment.
Also Read: How to Use Google Keep for Notes and To-Do Lists: Complete Beginner to Pro Guide
Why Block Websites Without Extensions?
Before learning the technical steps, it is useful to understand why built-in or system-level blocking methods are preferred over browser add-ons:
- Extensions can be bypassed by switching browsers or using incognito mode.
- Many schools and workplaces restrict extension installation.
- Extensions may collect usage data, which brings privacy concerns.
- System-level blocking affects all browsers, not just Chrome, Firefox, or Edge.
- Parents and guardians require stronger filtering for household devices.
This is why most cybersecurity experts recommend browser-independent blocking rather than extension-dependent solutions.
Method 1: Editing the Hosts File (Windows and macOS)
Editing the hosts file is one of the most powerful ways to block websites because it directly redirects domain names to your local machine instead of the actual internet server. Once configured, every browser on the device — Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari, and even in-app browsers — will refuse to load the blocked website.
How the Hosts File Method Works
The hosts file instructs the operating system to map web domains to specific IP addresses. By mapping unwanted domains to 127.0.0.1 (your own device), any attempt to load the site leads nowhere.
Steps for Windows
- Search for Notepad, right-click it, and choose Run as administrator.
- Navigate to:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\ - Select hosts (change file filter to All Files if needed).
- At the bottom, add entries like:
127.0.0.1 example.com127.0.0.1 www.example.com - Save the file.
- Open Command Prompt as administrator and run:
ipconfig /flushdns - Restart your device.
Steps for macOS
- Open Terminal.
- Enter:
sudo nano /etc/hosts - Type your admin password.
- Add lines such as:
127.0.0.1 www.example.com - Save with Control + O, press Enter, then exit with Control + X.
- Flush DNS using:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache - Restart your device.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Works across all browsers | Requires admin rights |
| Hard to bypass | Manual editing required |
| No additional software needed | Not ideal for blocking dozens of domains |
This is a preferred choice for tech-savvy users who want strict device-level blocking.
Method 2: Using Operating System Parental Controls
If the goal is to block unsafe websites for children or restrict browsing time, relying on built-in parental controls can be much easier than editing system files. Unlike extensions that kids can remove, parental controls require passwords to modify.
On Windows (Microsoft Family Safety)
- Go to Settings > Accounts > Family & other users.
- Add a child account if one does not exist.
- Open the Microsoft Family Safety dashboard online.
- Select the child profile.
- Navigate to Content filters.
- Enter domain names under Blocked websites.
The restrictions apply automatically across all Microsoft browsers, and in many cases, across third-party browsers too.
On macOS / iOS (Screen Time)
- Open System Settings (on iPhone, open Settings).
- Go to Screen Time.
- Enable Content & Privacy Restrictions and set a passcode.
- Select Web Content.
- Choose Limit Adult Websites or Allowed Websites Only.
- Add websites under the manual block list.
Why This Method Is Popular
Parental controls are ideal for:
- Safe browsing environments for minors
- School or library computers
- Personal productivity boundaries
- Shared household devices
It is one of the safest ways of applying restrictions while reducing the risk of bypassing.
Method 3: Blocking Sites Using Your Wi-Fi Router
If multiple users access the same network, device-level controls may not be enough. Router-level blocking ensures that no device on your Wi-Fi — laptops, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs — can access restricted domains.
How to Block Websites from the Router
- Find the router IP (commonly 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1).
- Open the IP in a web browser.
- Log in with the router admin username and password.
- Look for sections labeled:
- Parental Controls
- Access Restrictions
- Security Settings
- Add the domain names to the blocklist.
- Save the changes and restart the router if necessary.
Important Considerations
- Some routers block only HTTP websites and not HTTPS (newer routers block both).
- If users switch to mobile data, restrictions will not apply beyond the Wi-Fi network.
- For complete visibility, combine router-level security with device-level controls.
This method is especially effective for offices, schools, cyber cafés, and households with minors.
Also Read: How to Hide Apps on Android Without Uninstalling – Complete Guide
Method 4: Using DNS Filtering (OpenDNS and Similar Services)
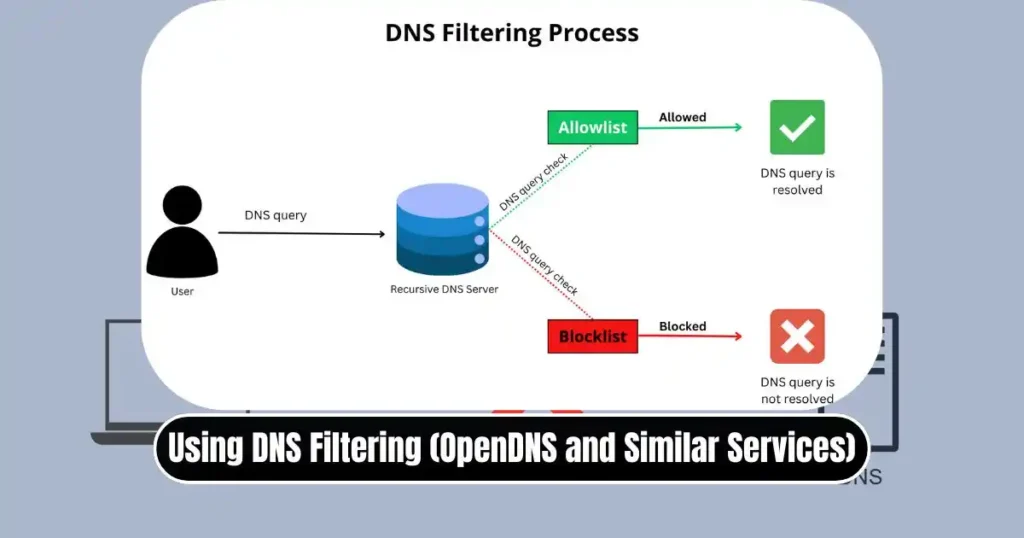
DNS filtering is a modern and highly scalable method. Instead of editing your router or operating system, you apply filters through a DNS provider that monitors and blocks websites based on categories and domain names.
How to Use OpenDNS to Block Websites
- Create a free account on OpenDNS.
- Change DNS settings on your device or router to:
208.67.222.222208.67.220.220
- Log in to the OpenDNS dashboard.
- Choose blocking preferences:
- Specific websites
- Adult content
- Social media
- Gaming
- Malware and phishing
- Save settings.
DNS filtering operates globally across devices and does not require constant maintenance.
Best Use Cases
- Parents who want category-based controls (e.g., blocking adult content)
- Business owners who want to increase productivity and cybersecurity
- School institutions that require safe learning environments
This solution offers both convenience and automation, making it more manageable than manually maintaining a list in the hosts file.
Method 5: Using Browser Privacy and Security Settings

While extensions add convenience, browsers also include built-in features that can restrict websites without third-party add-ons.
Google Chrome Options
- Safe Browsing: Filters harmful and inappropriate content
- Block JavaScript for specific sites: Makes targeted sites non-functional
- Admin-controlled URL blocking: Available in enterprise and education setups
To block JavaScript:
- Open Chrome Settings
- Go to Privacy and security > Site settings > JavaScript
- Add websites under Not allowed to use JavaScript
This does not remove the site entirely but makes it largely unusable.
For IT Administrators (Enterprise/Education)
Using admin.google.com, organizations can push URL-blocking policies to managed browsers. This ensures users cannot override settings locally.
Which Blocking Method Should You Use? (Comparison Table)
| Goal | Recommended Method |
|---|---|
| Complete blocking on one device | Hosts File |
| Children’s internet safety | Parental Controls |
| Blocking on all devices in the household | Wi-Fi Router |
| Preventing malware and unsafe categories | DNS Filtering |
| Blocking a few distracting sites like social media | JavaScript blocking in Chrome |
Every method has its purpose. Many users combine two or three approaches to maximize safety and productivity.
Also Read: How to Clear Cache on Android Phone: Easy Step-by-Step Guide
FAQs on How to Block Websites on Your Browser
1. Can blocked websites still load using VPN?
Yes. If a user activates a VPN, some block methods such as hosts file may be bypassed. Router-level and DNS filtering are more reliable against VPN bypassing.
2. Does blocking a website slow down the internet?
No. All methods described here work through DNS and system pathways that do not impact browsing speed.
3. Can someone remove website blocks without my permission?
If parental controls or router authentication are in place with a secure password, unauthorized users cannot disable blocks.
4. Which method is best for workplace controls?
Router-level blocking or centralized admin-controlled URL blocking is best for businesses and institutions.
5. Will the steps work on Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Brave?
Yes. All primary methods — hosts file, DNS filtering, and router blocking — apply regardless of browser.
Conclusion
Controlling what can and cannot be accessed online has become essential for digital safety, productivity, parental responsibility, and cybersecurity. Many users assume that extensions are the only option, but learning how to block websites on your browser without third-party add-ons offers stronger, more secure, and longer-lasting protection.
Whether someone edits the hosts file, configures router controls, uses parental restriction tools, sets up DNS filtering, or leverages browser privacy features, every method has a specific purpose. With the right approach — or a combination of approaches — individuals, families, and organizations can take full command of their browsing experience.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only. Website blocking techniques should not be used to violate institutional rules or legal regulations. Readers are responsible for complying with local laws, workplace policies, and ethical usage guidelines.
Also Read: How to Transfer Data From Old Phone to New Android – (Cable & Wireless)

Raj Prajapati is a skilled content writer dedicated to creating clear, step-by-step guides on technology, Health, and everyday solutions. With a focus on user-friendly and SEO-optimized content, he simplifies complex topics, helping readers learn and solve problems effortlessly.

